Build push notifications for an app built with XMTP
The XMTP framework's notification architecture, in conjunction with Firebase Cloud Messaging, offers a secure and reliable approach to notification management and delivery.
This guide describes the essential steps to build push notifications, from device registration to message decryption, along with a detailed explanation of each step and code examples.
To help illustrate a push notification scenario, consider a message Alix sends to Bo using a mobile messaging app. Al app is built with React Native for iOS devices and uses Firebase for notifications.
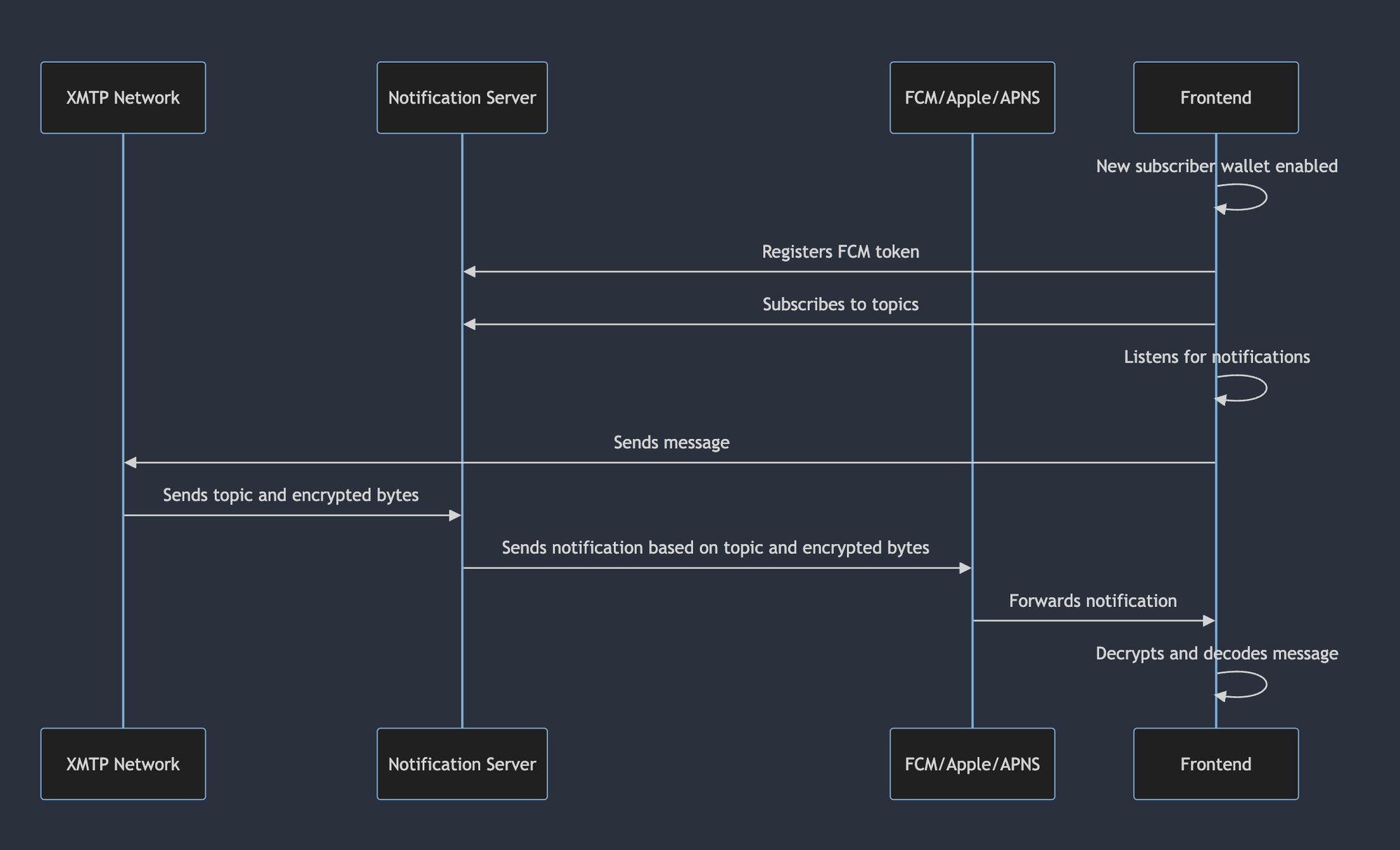
Notifications architectural overview
Understand Apple entitlements for iOS apps
When building an iOS app with XMTP, you might want to suppress certain Apple push notifications. For example, you should suppress push notifications for a user's own messages.
You can use the com.apple.developer.usernotifications.filtering entitlement. To do so, you need to obtain permission from Apple. Submit the application using the app owner's Apple developer account via https://developer.apple.com/contact/request/notification-service.
Here are some sample answers to help you complete the application:
- App name: [Your app name]
- App Store URL: [Your app store URL]
- Apple ID of App: [Your app ID]
- App Type: Messaging
- Does your app provide end-to-end encryption?: Yes
- Explain why existing APIs are not adequate for your app: The existing APIs always show some sort of notification when a push comes in. We don't want to show a notification for a user's own messages.
- Explain why your app doesn’t show a visible notification each time a push notification is received: The server delivering notifications only knows of the existence of a conversation. It does not know who the sender or recipient are. That data is decoded on the device in the extension. As a result, it sends a push notification for every message that occurs in the conversation. We want to filter out notifications for notifications that the user sent.
- When your extension runs, what system and network resources does it need?: We might need to make a GRPC request in order to load additional information about a conversation. This is only necessary when we haven't stored the conversation details locally, which is expected to be less common than being able to just decode the conversation locally.
- How often does your extension run? What can trigger it to run?: The extension will run whenever a message is sent or received in a conversation. The frequency will depend on how active a user is.
1. Initialize the XMTP client
Alix opens the frontend on their iOS device and initializes their new wallet with XMTP.
import { Client } from "@XMTP"; // XMTP JavaScript client
// Alix initializes their wallet on the Frontend
const XMTPClient = await Client.create(aliceSigner, { env: "dev" });2. Register the device with Firebase
When Alix launches the frontend on their device for the first time, the app registers with Firebase to receive notifications.
// Get token from Firebase
const deviceToken = await messaging().getToken();
// Get unique ID for the device
const installationId = await installations().getId();
// Assume this function sets up your notification client
const client = createNotificationClient();
await client.registerInstallation({
installationId,
deliveryMechanism: {
deliveryMechanismType: {
value: deviceToken,
case: "FirebaseDeviceToken",
},
},
});3. Subscribe to topics
The notification server adds Alix's installationId to certain topics. The list of subscriptionDetails includes all information needed to join topics, such as user permission and HMAC keys for safely checking messages.
-
consentState: Notifications are only subscribed to if theconsentStateof a conversation is "allowed". This ensures that users receive notifications only for conversations they have consented to. Learn more -
Invitetopic V2: Clients use invite topics to initiate conversations between wallets. Learn more -
Introtopic V1: Clients use intro topics to store the first message sent between two wallets
let subscriptionDetails = [];
// Filter conversations to only include those with user consent, to respect privacy and avoid SPAM.
const consentedConversations = conversations.filter(
(conversation) => conversation.consentState === "allowed",
);
// Compile the subscription info, attaching the HMAC key when available.
consentedConversations.forEach((conversation) => {
subscriptionDetails.push({
topic: conversation.topic,
hmacKey: conversation.hmacKey || null,
});
});
// Special topics without HMAC keys
subscriptionDetails.push({
topic: buildUserInviteTopic(userAddress),
hmacKey: null,
});
subscriptionDetails.push({
topic: buildUserIntroTopic(userAddress),
hmacKey: null,
});
// This operation sends the subscription details to the notification service.
await notificationClient.subscribeWithMetadata({
installationId,
subscriptions: subscriptionDetails,
});4. Listen for notifications
Alix's frontend is now listening for incoming notifications.
// Listener for incoming Firebase notifications
messaging().onMessage(async (remoteMessage) => {
console.log("A new message arrived!", remoteMessage);
});5. Send a message
Bo sends a message to Alix using their instance of the frontend.
const bobClient = await Client.create(bobSigner, { env: "dev" });
const conversation = await bobClient.conversations.newConversation(aliceWallet);
await conversation.send("Hello Alix!");6. XMTP network dispatch
The XMTP network sends the encrypted message and topic to the notification server.
// Pseudo-code for XMTP network sending encrypted message
const messageTopic = "XMTP/0/dm-alice-XMTP-topic-id";
sendToNotificationServer(encryptedMessage, messageTopic);7. Trigger push notifications
The notification server triggers a push notification to Firebase.
const message = {
data: {
topic: messageTopic,
message: encryptedMessage,
},
topic: messageTopic,
};
firebase_admin.messaging().send(message);8. Firebase notification forwarding
Firebase forwards the notification to Alix's device.
9. Decrypt the message
Alix's frontend receives the notification and decrypts the message.
// Decrypting the message when a notification is received from Firebase
Firebase.messaging().onMessage((payload) => {
const decryptedMessage = decryptMessage(payload.data.message, encryptionKey);
console.log("Decrypted message:", decryptedMessage);
});
